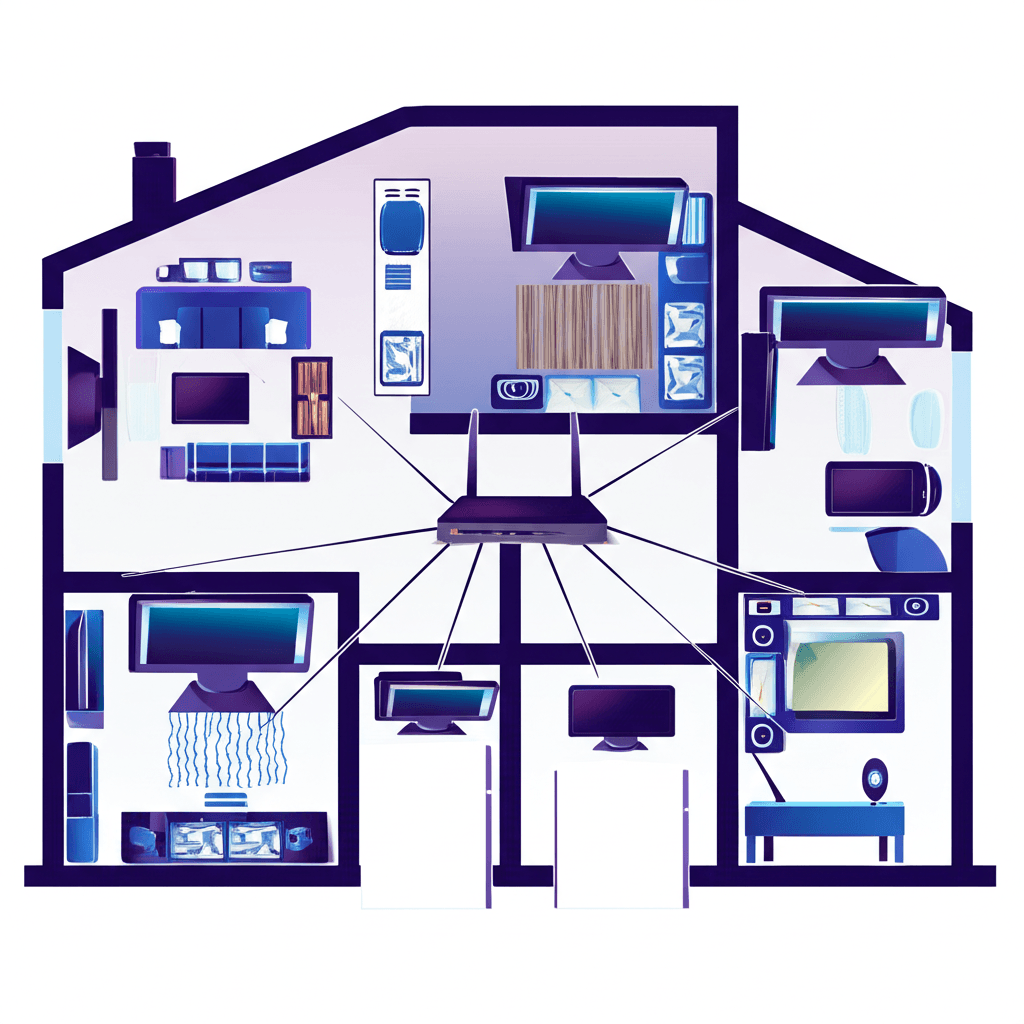
Modern households often have televisions in multiple rooms—living rooms, bedrooms, kitchens, even outdoor spaces. IPTV multi-room setups enable streaming television access throughout the home, allowing family members to watch their preferred content wherever they are. Planning and implementing effective whole-home IPTV requires understanding network requirements, device options, and subscription considerations.
Understanding Multi-Room IPTV
Multi-room IPTV extends television streaming capability to every viewing location in your home. Unlike traditional cable systems requiring physical coaxial connections to each TV, IPTV distributes content over your existing home network. Any network-connected device with an appropriate IPTV application can access your streaming service.
The foundation of multi-room IPTV lies in simultaneous connection support. Standard IPTV subscriptions often allow only one active stream, requiring you to stop viewing in one room before starting in another. Multi-room plans permit several concurrent streams, enabling different family members to watch different content simultaneously across the home.
Each viewing location needs a compatible device—streaming boxes, smart TVs with IPTV apps, or connected game consoles. These devices connect to your home network and communicate with IPTV servers to receive and display video content. The subscription credentials configure all devices, though each active stream counts against your concurrent connection limit.
Planning Your Multi-Room Setup
Effective multi-room IPTV begins with planning that considers viewing locations, device types, network infrastructure, and usage patterns. Thorough planning prevents problems and ensures satisfactory performance throughout the home.
Start by identifying all current and potential viewing locations. Common spots include living rooms, bedrooms, kitchens, home offices, and outdoor patios. Consider both primary viewing areas where high-quality streaming matters most and secondary locations where occasional viewing occurs. This inventory informs device selection and network planning.
Evaluate existing network infrastructure. Note router location, current WiFi coverage, and any existing ethernet runs. Identify areas with weak WiFi signal that might need enhancement. Consider whether your current internet plan provides sufficient bandwidth for planned simultaneous streams.
Assess typical viewing patterns to determine required concurrent connections. If family members rarely watch simultaneously, fewer connections might suffice. Households where everyone watches different content at the same time need plans supporting that usage. Peak viewing times—evenings and weekends—reveal true simultaneous usage requirements.
Network Infrastructure Requirements
Reliable multi-room IPTV demands robust network infrastructure capable of delivering multiple high-quality video streams throughout your home. Network performance directly impacts viewing experience, making infrastructure investment worthwhile.
Internet bandwidth requirements scale with simultaneous streams. Standard definition streams need approximately 3-5 Mbps each. High definition requires 8-12 Mbps per stream. Full HD 1080p content uses 12-18 Mbps, while 4K demands 25-35 Mbps per stream. Calculate total requirements based on maximum expected simultaneous usage, adding 25-50% headroom for other household internet activities.
Router capabilities significantly impact multi-stream performance. Consumer-grade routers often struggle managing multiple simultaneous video streams. Look for routers with dual-band or tri-band WiFi, MU-MIMO (multi-user multiple input multiple output) technology, and Quality of Service (QoS) features that prioritize streaming traffic.
WiFi coverage must reach all viewing locations with adequate signal strength. Large or multi-story homes often need WiFi extenders or mesh network systems to eliminate dead zones and weak signal areas. Poor WiFi leads to buffering and quality degradation that ruins the viewing experience.
WiFi vs Ethernet Connections
The choice between WiFi and ethernet connections for each viewing location affects reliability, performance, and installation complexity. Both approaches have valid applications in multi-room setups, and hybrid configurations often prove optimal.
Ethernet connections provide maximum reliability and performance. Wired connections eliminate WiFi interference issues, maintain consistent speeds, and introduce minimal latency. For primary viewing locations where streaming quality matters most—typically living rooms and main bedrooms—ethernet connections are worth the installation effort.
Running ethernet cables requires either during-construction installation or retrofit work. In-wall cable runs provide cleanest results but require more effort. Surface-mounted cable channels or cables run along baseboards offer easier installation. Powerline adapters use electrical wiring to carry network signals, providing a middle ground when running cables proves impractical.
WiFi connections offer flexibility and simpler installation. Modern WiFi 6 (802.11ax) routers and devices provide sufficient bandwidth for HD and even 4K streaming when signal strength is adequate. WiFi suits secondary viewing locations, mobile devices, and areas where running cables is prohibitively difficult.
Mesh WiFi for Whole-Home Coverage
Mesh WiFi systems have revolutionized whole-home network coverage, making them particularly valuable for multi-room IPTV deployments. Unlike traditional routers with optional extenders, mesh systems create seamless coverage through multiple coordinated nodes.
Mesh networks consist of a primary router unit connected to your modem plus additional satellite nodes placed throughout the home. These nodes communicate with each other, creating overlapping coverage areas. Devices automatically connect to whichever node provides the strongest signal, enabling movement throughout the home without connection drops.
Popular mesh systems from brands like Eero, Google Nest WiFi, Netgear Orbi, and TP-Link Deco offer varying capabilities and price points. Higher-end systems include tri-band configurations with dedicated backhaul channels, ensuring node-to-node communication doesn't compete with device traffic.
Plan mesh node placement strategically. Central home locations provide better coverage than corner placements. Nodes should have clear sight lines to each other when possible, avoiding placement behind large obstacles. Two to three nodes suffice for typical homes; larger properties may need four or more for complete coverage.
Choosing Devices for Each Room
Different rooms may warrant different streaming devices based on viewing importance, TV capabilities, and budget considerations. Matching device capabilities to room requirements optimizes both cost and experience.
Primary viewing rooms deserve premium devices. Amazon Fire TV Stick 4K Max, NVIDIA Shield TV, or Apple TV 4K offer powerful processors for smooth navigation, 4K HDR support, and responsive remote controls. These devices provide the best IPTV application compatibility and premium features like voice control.
Secondary bedrooms and casual viewing areas work well with mid-tier devices. Standard Fire TV Stick, Roku Express, or Chromecast with Google TV provide solid IPTV performance at lower costs. These devices may lack 4K on older TVs anyway, making premium features unnecessary.
Kitchen and utility areas often feature smaller screens for background viewing while cooking or exercising. Basic streaming sticks suffice, though consider rugged or splash-resistant options for areas prone to moisture. Small tablets mounted on walls offer flexible alternatives to traditional TV setups.
Smart TVs with built-in apps eliminate the need for external streaming devices in some cases. Many modern smart TVs run Android TV or support app installations including IPTV players. However, external devices often outperform built-in TV processors and receive more consistent software updates.
Configuring Multiple Devices
Setting up IPTV on multiple devices involves installing applications and entering credentials on each unit. While each device needs individual configuration, consistent setup across devices simplifies household usage.
Choose the same IPTV application across all devices when possible. Using IPTV Smarters Pro or TiviMate on every streaming device creates familiar interfaces throughout the home. Family members moving between rooms encounter the same navigation and organization regardless of which TV they use.
Synchronize favorites and channel organization across devices. Some IPTV applications support cloud synchronization of favorites lists. Otherwise, manually configure each device with the same favorites and channel ordering. This consistency reduces confusion when switching between rooms.
Consider device naming conventions that identify room locations. Naming devices "Living Room Fire Stick" or "Bedroom TV" helps track connections through IPTV provider dashboards and simplifies troubleshooting when issues arise.
Managing Subscription Connections
Multi-room setups require careful attention to subscription connection limits. Understanding how connections work prevents frustration when devices unexpectedly can't connect because limits are reached.
Connection limits count active streams, not registered devices. You might configure ten devices throughout your home, but a 4-connection plan allows only four to stream simultaneously. Devices not actively streaming don't count against limits—starting a stream on the living room TV while others are inactive consumes only one connection.
Properly stopping streams instead of just turning off TVs frees connections promptly. Some devices continue streaming when TVs power off unless apps are properly closed. Train household members to exit IPTV applications before turning off TVs, ensuring connections release for other devices.
Monitor connection usage if your provider offers dashboard access. Seeing which devices currently consume connections helps troubleshoot situations where new streams won't start. Identifying patterns of connection usage informs whether current limits suffice or whether upgrading makes sense.
Bandwidth Management Strategies
With multiple simultaneous streams potentially running, managing bandwidth prevents any single room's viewing from degrading others. Several strategies help maintain quality across all viewing locations.
Quality of Service (QoS) router settings prioritize streaming traffic over less time-sensitive activities like file downloads or cloud backups. Configure your router's QoS to recognize IPTV traffic and allocate bandwidth accordingly. This ensures streams maintain quality even during heavy network usage.
Stream quality settings in IPTV applications allow matching quality to available bandwidth and TV capabilities. A small kitchen TV doesn't need 4K streams—reducing to HD or SD conserves bandwidth for other rooms. Primary TVs can stream at maximum quality while secondary rooms use lower settings.
Scheduled activities that consume bandwidth—like system updates, game downloads, or cloud backups—can be scheduled for overnight hours when streaming demand is lowest. This prevents competition between essential household internet activities and evening entertainment viewing.
Troubleshooting Multi-Room Issues
Multi-room setups introduce complexity that can cause issues not present with single-device configurations. Systematic troubleshooting isolates problems and identifies solutions.
Room-specific buffering usually indicates network issues in that location. Test WiFi signal strength using phone apps—weak signal requires extender placement or mesh node addition. If using WiFi, try temporarily connecting the device via ethernet to determine whether the problem is WiFi-related or more fundamental.
Simultaneous streaming failures may indicate connection limit exhaustion. Verify all household members' devices are accounted for—sometimes forgotten background streams on tablets or phones consume connections. Ensure no unauthorized devices have access to your credentials.
Whole-home performance issues point to internet bandwidth problems or router limitations. Test direct internet speeds to verify your provider delivers promised bandwidth. During peak usage, run speed tests to identify throttling or congestion issues that might warrant plan upgrades or provider discussions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many TVs can I connect to one IPTV subscription?
The number of TVs depends on your subscription plan's connection limit. Single-connection plans support one TV at a time, while family plans typically allow 2-5 simultaneous streams. Premium multi-room plans may support 10 or more concurrent connections. Each TV needs its own streaming device configured with your IPTV credentials.
Do I need ethernet for multi-room IPTV or will WiFi work?
WiFi can work for multi-room IPTV if you have a strong, modern network. However, ethernet provides more reliable performance, especially when streaming to multiple rooms simultaneously. Consider using mesh WiFi systems for larger homes or running ethernet cables to rooms with primary viewing TVs for optimal results.
What internet speed do I need for multi-room IPTV?
Plan for approximately 10-15 Mbps per HD stream. A home with four TVs potentially streaming simultaneously needs at least 50-75 Mbps for comfortable HD viewing plus headroom for other internet activities. For 4K content, increase estimates to 25-35 Mbps per stream.
Can each TV watch different channels at the same time?
Yes, with a multi-connection plan, each TV operates independently. Family members can watch completely different channels, VOD content, or recordings simultaneously. The TV in the living room can show sports while bedrooms watch movies—all from the same IPTV subscription but using separate connection slots.